RF & Microwave Connectors and Transitions Simulation
High-frequency EM simulation of RF connectors and transitions
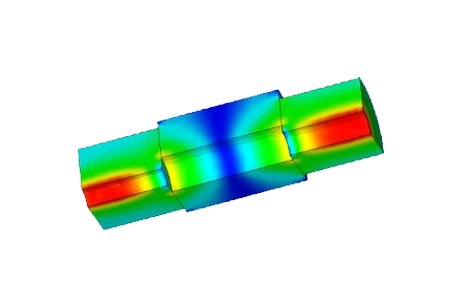
This note uses the RF & Microwave module to analyze a coaxial cable with discontinuities, deriving TDR impedance profiles from S-parameters to locate and interpret mismatches.
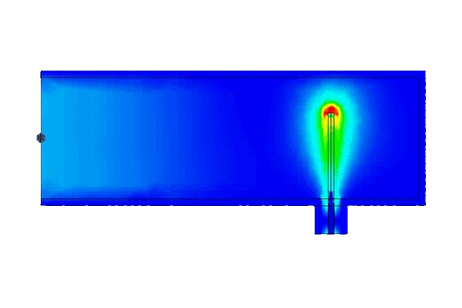
This note uses EMWorks to model a 2.4 GHz rectangular waveguide-to-coax adapter, computing return loss, power transfer, and E/H-field distributions inside the transition.
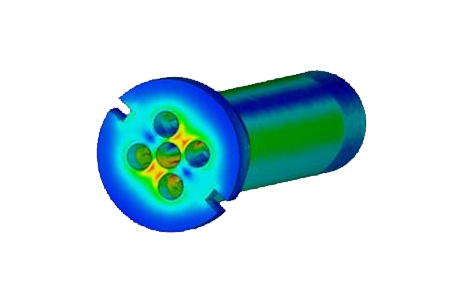
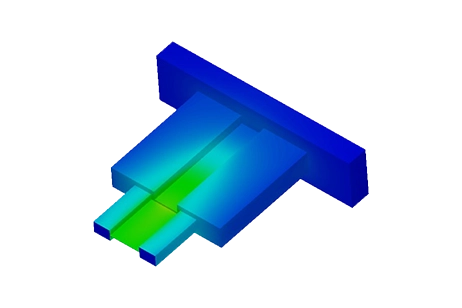
This application note demonstrates how to simulate a 100 Mbps Ethernet Quadrax connector in EMWorks, using an S-parameter study from 100 MHz to 2.5 GHz. You can assess insertion and return losses, visualize near and internal electric field distributions, and verify that the connector meets high-speed signal integrity requirements in dense, harsh-environment networks.
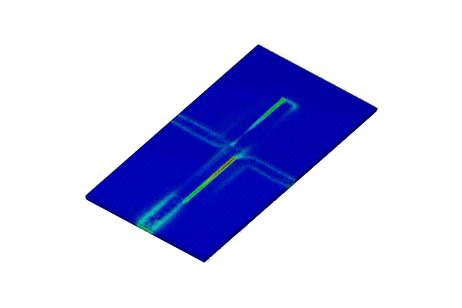
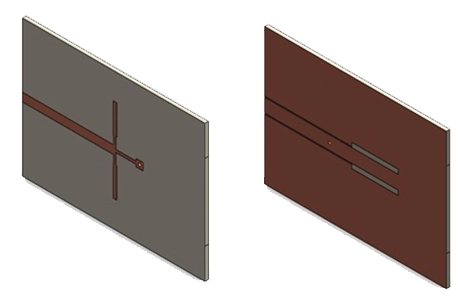
This application note models a planar Marchand balun centered at 2.4 GHz with 1 GHz bandwidth on RO4003. Using 3D S-parameter analysis, it verifies equal power division, 180° phase shift between outputs, and acceptable return loss from 1 to 4 GHz. Field plots and impedance checks help validate the layout before fabrication.
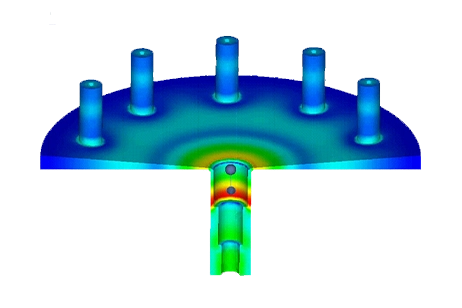
This application note simulates a 10-way conical power combiner from 2 to 20 GHz and compares S-parameters to published measurements. The study reports return loss, insertion loss, and output port isolation, using refined meshing at discontinuities to capture impedance transitions accurately.
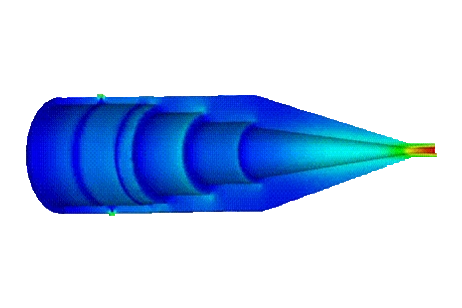
This application note validates an eight-way coaxial power combiner from 0.5 to 2 GHz by comparing HFWorks S-parameter simulations with published measurements. The study reports return loss, insertion loss, and output port isolation, using refined meshing near the stepped-impedance matching section and ports to capture impedance transitions accurately.
This application note presents the design and analysis of a half-height WR2300 ridge waveguide coupler used to feed accelerator cavities. Cutoff frequency versus ridge gap is studied for the TE10 mode, and simulated return and insertion losses are compared with measurements, confirming resonance at 0.353 GHz. An RF-to-thermal analysis under 250 kW incident power evaluates conductor losses and temperature distribution, demonstrating negligible temperature rise and no thermal-structural issues in the coupler.
Simulate thick wire bonds in EMWorks to evaluate temperature rise, mechanical deflection, and failure risk under DC current. The model couples magnetostatic, steady-state thermal, and structural analysis on wire, copper layers, and alumina substrate.