Introduction
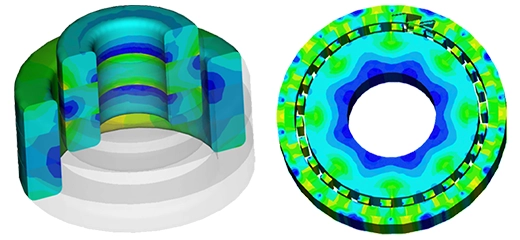
The automotive industry is undergoing a transformative shift towards electrification, driven by the need for cleaner, more efficient, and sustainable transportation solutions. One of the most promising advancements in this space is the development of in-wheel electric motors. Unlike traditional electric vehicles (EVs) that use a central motor connected to the wheels via a transmission system, in-wheel motors integrate the motor directly into the wheel hub. This design offers numerous advantages, including improved efficiency, enhanced vehicle dynamics, and greater design flexibility. Fujishiro et al. conducted a study designing three outer-rotor multipolar switched reluctance (SR) motors and analyzed their characteristics using finite element method (FEM) simulations as shown in Fig. 2 [1].
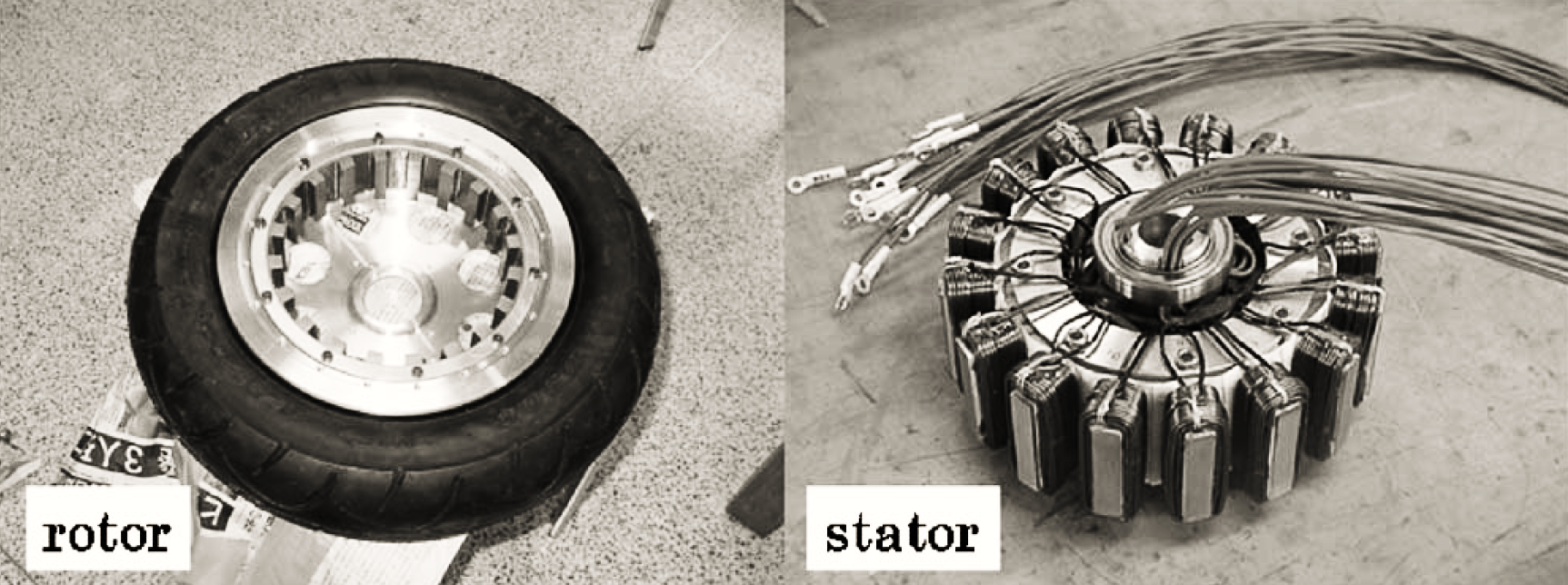

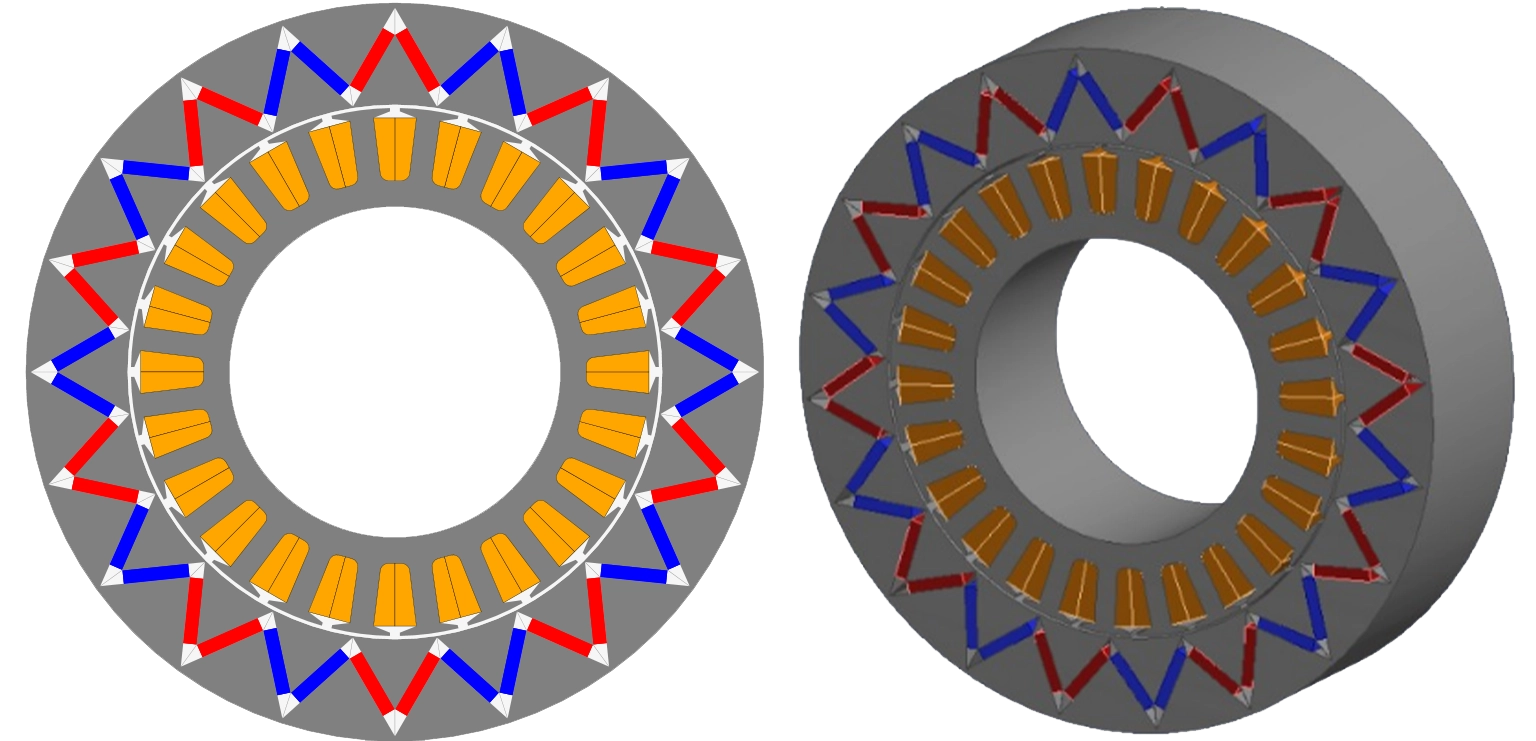
In this blog, we will explore the design of an outer rotor in-wheel electric motor with a 24-slot 20-pole configuration as shown in Fig. 2. We will discuss the benefits of in-wheel motors, the design process, and the simulation results obtained using EMWORKS MOTORS software. By the end of this blog, you will have a clear understanding of how to design and analyze an in-wheel motor, as well as how EMWORKS MOTORS can streamline the design process for engineers.
Applications of In-Wheel Motors and Their Benefits
In-wheel motors are particularly well-suited for a variety of applications as shown in Fig. 3, including:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): In-wheel motors are increasingly being used in passenger cars, buses, and trucks. They offer a compact and efficient solution for electrifying vehicles without the need for complex drivetrains.
- Autonomous Vehicles: The precise control offered by in-wheel motors makes them ideal for autonomous vehicles, where independent control of each wheel can enhance stability and maneuverability.
- Electric Bicycles and Scooters: In-wheel motors are commonly used in electric bicycles and scooters due to their simplicity and compact design.
- Robotics: In-wheel motors are also used in robotic applications, where precise control and compact design are critical.
Benefits Over Traditional Motor Designs
In-wheel motors provide several significant advantages over traditional central motor designs that rely on transmission systems. One of the most notable benefits is improved efficiency, as the elimination of a transmission system reduces mechanical losses, resulting in higher overall energy efficiency. Additionally, in-wheel motors enable enhanced vehicle dynamics through independent control of each wheel, allowing for advanced features like torque vectoring. This capability improves handling, stability, and safety, particularly in challenging driving conditions. Another advantage is the space savings they offer; by integrating the motor directly into the wheel, in-wheel motors free up valuable space within the vehicle chassis. This allows for more flexible interior design and additional room for storage or battery placement, which is especially beneficial for electric vehicles.
Furthermore, the absence of a transmission system simplifies the vehicle's mechanical design, reducing the number of moving parts and potentially lowering maintenance costs over the vehicle's lifespan. Lastly, in-wheel motors seamlessly incorporate regenerative braking, a feature that captures energy during braking and stores it in the battery, further enhancing the vehicle's efficiency and range. These combined benefits make in-wheel motors a compelling choice for modern electric and autonomous vehicles.
Design of an Outer Rotor In-Wheel Motor with 24 Slots and 20 Poles
When designing an in-wheel motor, several key factors must be considered:
In an outer rotor design, the rotor is located on the outside of the motor, while the stator is fixed to the wheel hub. This configuration is well-suited for in-wheel applications because it allows for a larger rotor diameter, which can generate higher torque. The choice of slots and poles is critical for achieving the desired performance characteristics. A 24-slot, 20-pole configuration is a common choice for in-wheel motors because it offers a good balance between torque density, efficiency, and manufacturability.
Design Steps
Initial Sizing and Specifications: The first step in designing an in-wheel motor is to define the key specifications, such as the required torque, speed, power, and efficiency. These specifications will guide the selection of the motor's dimensions, materials, and winding configuration as shown in Fig. 5.
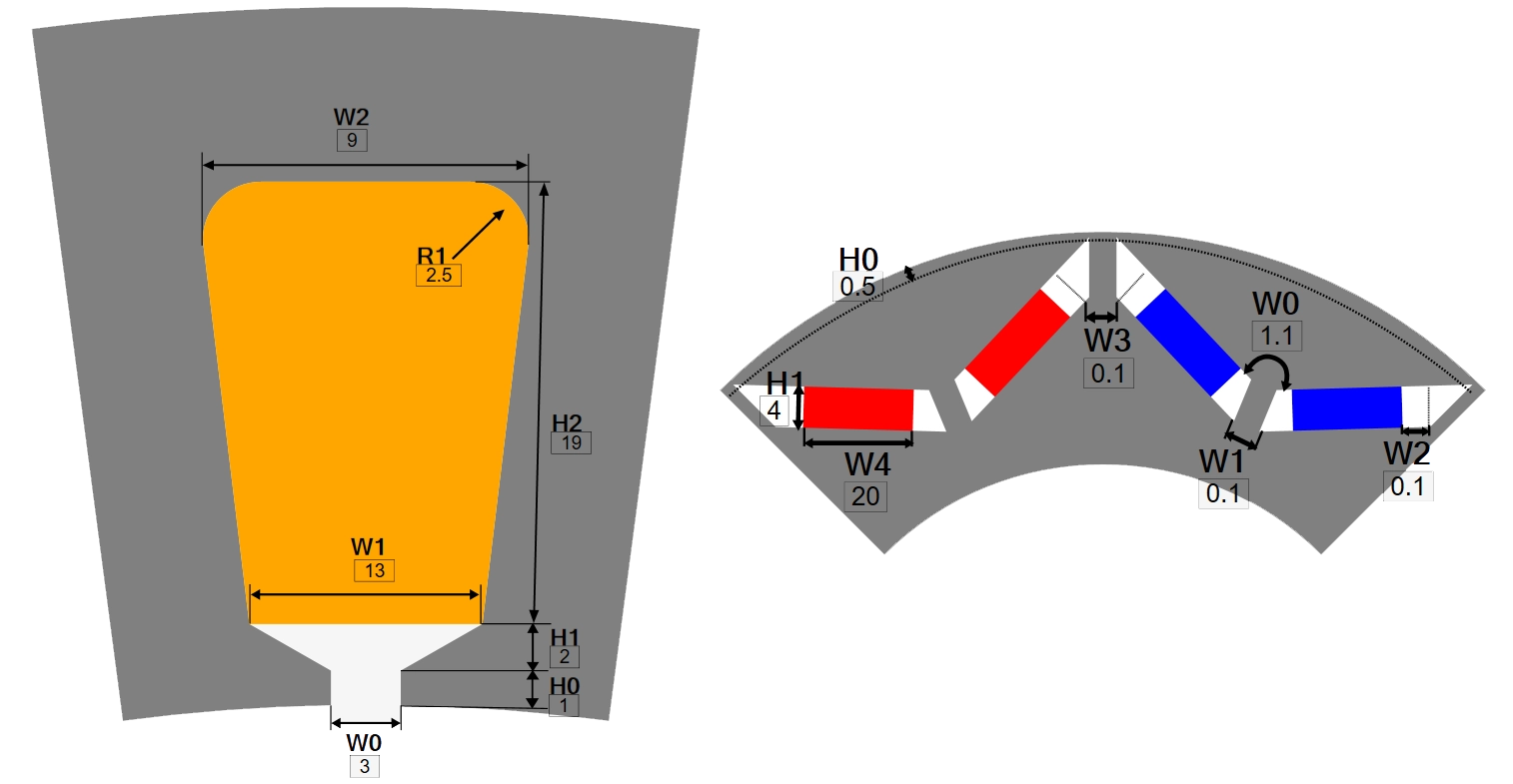
Electromagnetic Design: Using EMWORKS MOTORS software, the electromagnetic design of the motor can be optimized as shown in Fig 6. This includes selecting the number of slots and poles, determining the winding pattern, and optimizing the magnetic circuit to achieve the desired performance.
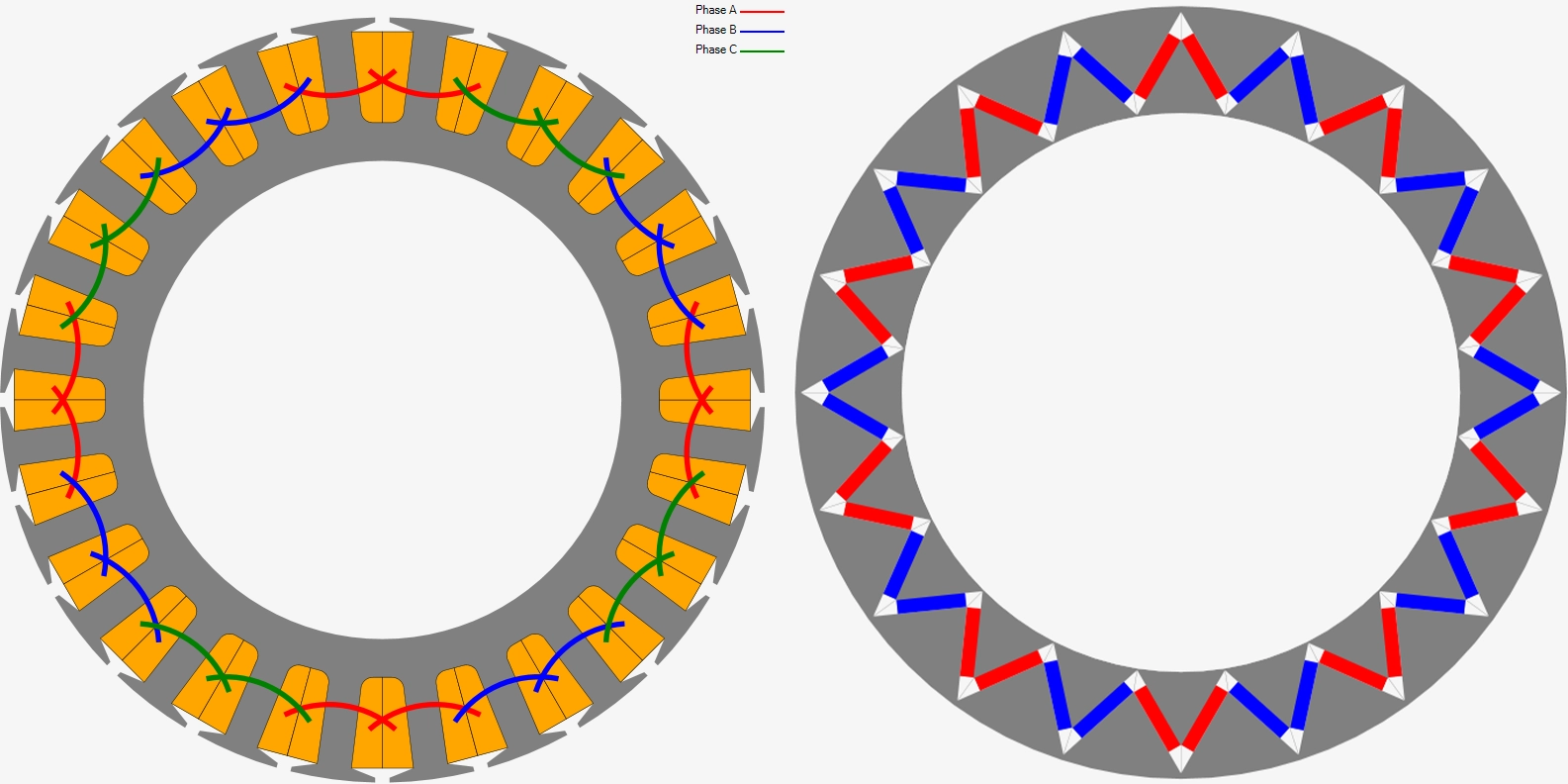
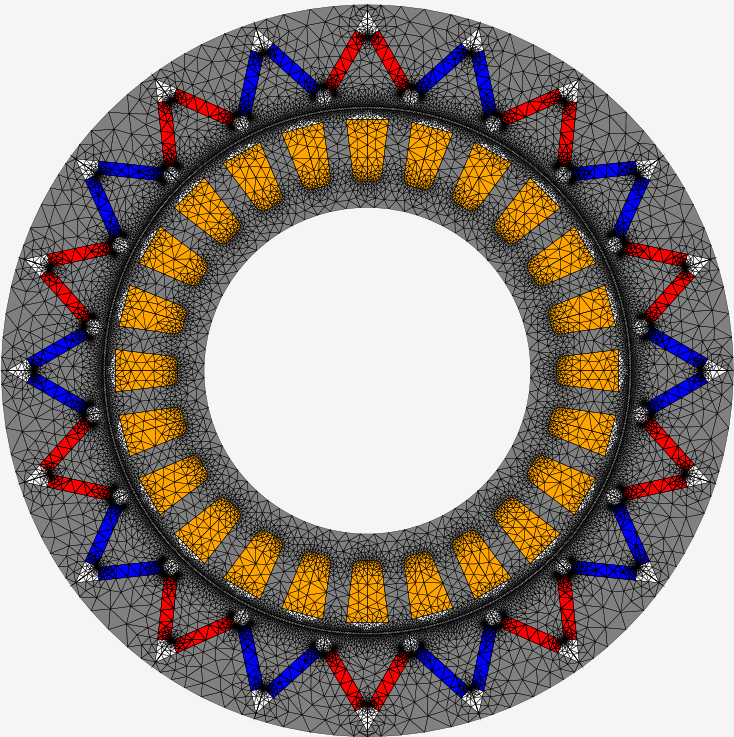
Performance Simulation: Once the design is finalized, EMWORKS MOTORS can be used to simulate the motor's performance, including back EMF, torque, magnetic flux density, and efficiency. These simulations provide valuable insights into the motor's behaviour and allow for further optimization.
Simulation Results
Using EMWORKS MOTORS software, we can obtain a range of simulation results that provide valuable insights into the performance of the in-wheel motor:
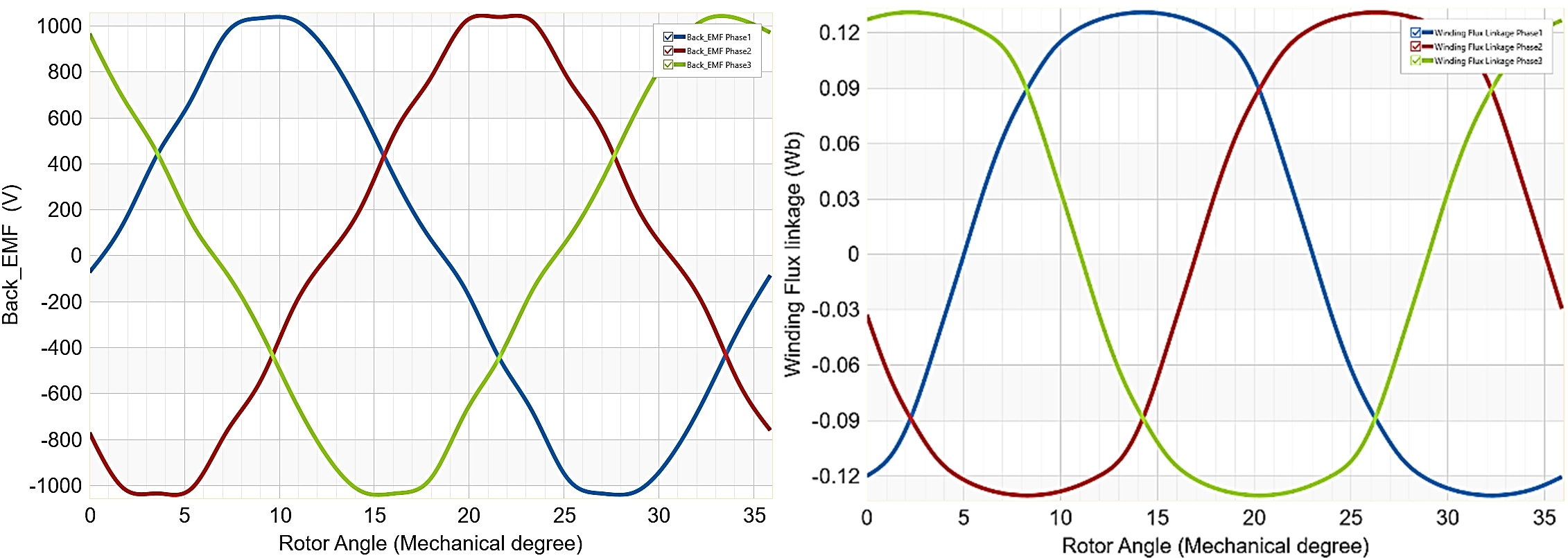
Back EMF and Flux Linkage: The back EMF waveform is a key indicator of the motor's electrical performance. A well-designed motor will have a sinusoidal back EMF waveform, which minimizes torque ripple and improves efficiency. The amplitude of the back-EMF reaches approximately 1000 V, indicating the voltage generated by the motor as the rotor spins.
The flux linkage waveform is sinusoidal, with an amplitude of approximately 0.12 Wb. The sinusoidal flux linkage indicates that the magnetic coupling between the rotor and stator is well-balanced as shown in Fig. 7.
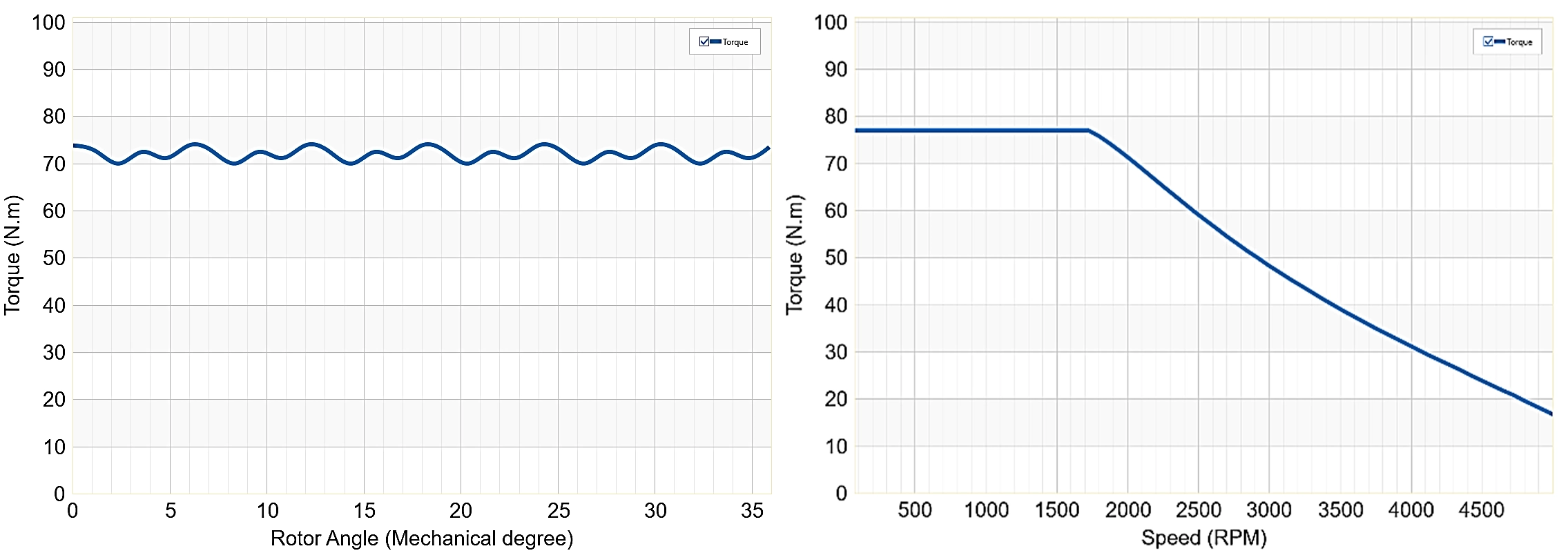
Torque: The torque output of the motor is critical for vehicle performance. EMWORKS MOTORS allows engineers to simulate the motor's torque characteristics, including peak torque and torque ripple, to ensure that the motor meets the required performance specifications as shown in Fig. 8. This result helps in optimizing the motor’s operating range and ensuring it performs efficiently across different speed conditions.
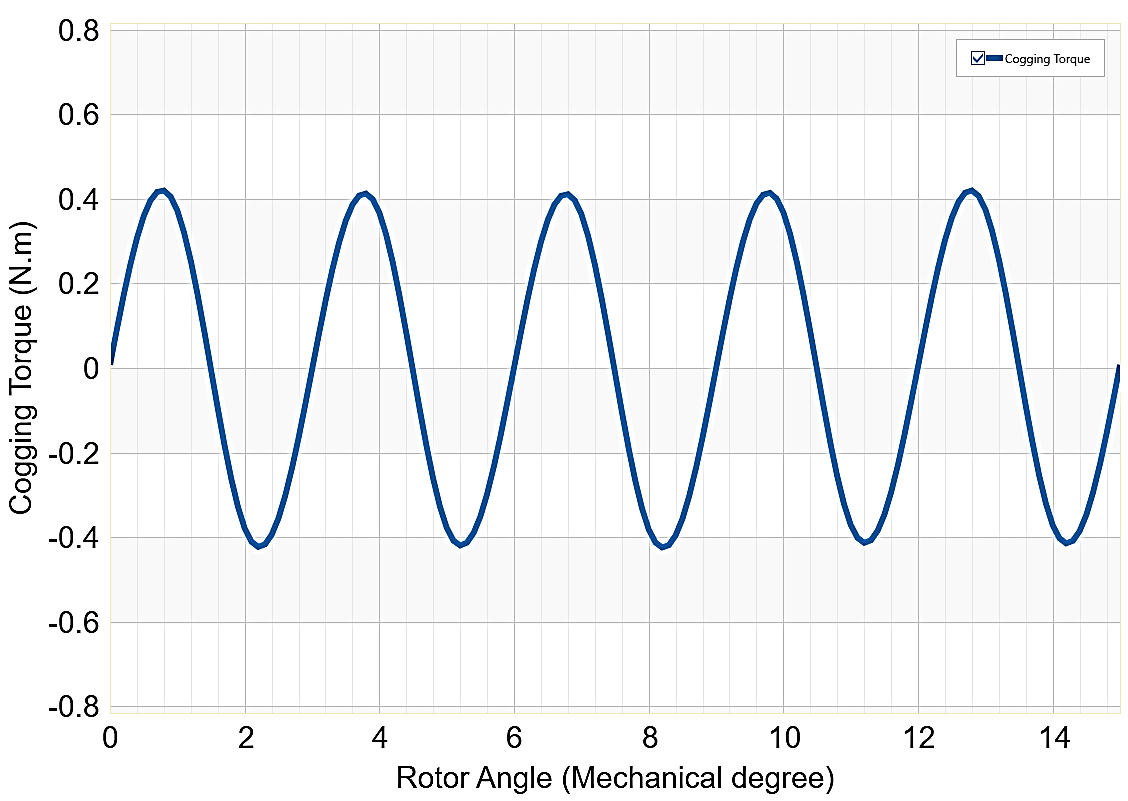
The periodic torque waveform indicates the presence of torque ripple, which is common in PMSMs due to the interaction between the rotor magnets and stator slots. The cogging torque waveform has a small amplitude, ranging from approximately -0.4 N.m to 0.4 N.m. as shown in Fig. 9. Cogging torque is caused by the interaction between the rotor magnets and stator slots, leading to small fluctuations in torque even when the motor is not energized.
The low amplitude of the cogging torque in this motor indicates a well-designed stator and rotor configuration, which minimizes unwanted vibrations and noise. Reducing cogging torque is essential for applications requiring a smooth operation, such as electric vehicles or precision machinery.
How EMWORKS MOTORS Software is Helping Engineers Design Motors
EMWORKS MOTORS is a powerful tool that is revolutionizing the way engineers design electric motors. Here are some of the key features that make EMWORKS MOTORS an invaluable resource for motor design as shown in Fig. 10:
Comprehensive Simulation Capabilities: EMWORKS MOTORS offers a wide range of simulation capabilities, including electromagnetic, thermal, and structural analysis. This allows engineers to perform a complete analysis of the motor's performance in a single software environment.
User-Friendly Interface: EMWORKS MOTORS features an intuitive interface that makes it easy for engineers to set up and run simulations. The software also includes a range of pre-built templates and design wizards that streamline the design process.
High Accuracy: EMWORKS MOTORS uses advanced numerical methods to ensure high accuracy in its simulations. This allows engineers to have confidence in the results and make informed design decisions.
Integration with CAD Software: EMWORKS MOTORS can be easily integrated with popular CAD software, allowing engineers to import and export motor designs seamlessly. This integration simplifies the design process and reduces the risk of errors.
Cost-Effective: By providing a comprehensive set of simulation tools in a single software package, EMWORKS MOTORS helps engineers reduce the time and cost associated with motor design. This makes it an attractive option for both large manufacturers and small startups.
Conclusion
In-wheel motors represent a significant advancement in electric vehicle technology, offering numerous benefits over traditional motor designs. By integrating the motor directly into the wheel, engineers can achieve higher efficiency, improved vehicle dynamics, and greater design flexibility. However, designing an in-wheel motor requires careful consideration of electromagnetic, thermal, and mechanical factors.
EMWORKS MOTORS software is an invaluable tool for engineers designing in-wheel motors. Its comprehensive simulation capabilities, user-friendly interface, and powerful optimization tools make it easier than ever to design and analyze high-performance electric motors. Whether you're designing a motor for an electric vehicle, an autonomous robot, or an electric bicycle, EMWORKS MOTORS can help you achieve your design goals quickly and efficiently.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, in-wheel motors are poised to play a key role in the future of transportation. With the help of advanced design tools like EMWORKS MOTORS, engineers can push the boundaries of what's possible and create innovative solutions that drive us toward a cleaner, more sustainable future.
References:
[1] Fujishiro, Satoshi & Ishikawa, Kazumi & Kikuchi, Shinki & Nakamura, Kenji & Ichinokura, Osamu. (2006). Design of outer-rotor-type multipolar switched reluctance motor for electric vehicle. Journal of Applied Physics. 99. 08R324 - 08R324. 10.1063/1.2172180.
[2] Abdoos, A., Moazzen, M., & Hosseini, S. (2021). Optimal Design of an Exterior-Rotor Permanent Magnet Generator for Wind Power Applications . Journal of Operation and Automation in Power Engineering, 9(3), 193-202. doi: 10.22098/joape.2021.7337.1532
[3] Mamur, Hayati & Sahin, Cihan & Karacor, Mevlut & Bhuiyan, Mohammad. (2020). Design and fabrication of an outer rotor permanent magnet synchronous generator with fractional winding for micro-wind turbines. IET Electric Power Applications. 14. 2273-2282. 10.1049/iet-epa.2020.0318.