Introduction
Electrical machines are typically categorized as either radial or axial flux machines. Radial flux machines have been prevalent for quite some time, while axial flux machines have gained popularity primarily over the last two decades. The key distinction lies in their flux direction: axial flux machines have a magnetic flux direction parallel to the machine's rotation axis, whereas radial flux machines have a radial magnetic flux direction.
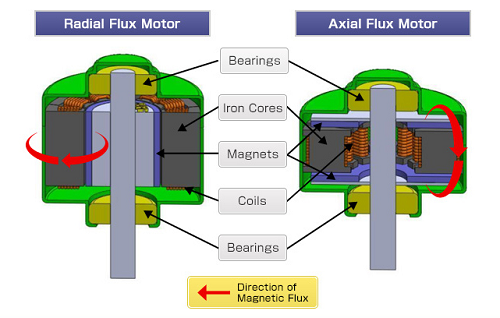

Why Axial flux machine is considered superior to a Radial flux machine?
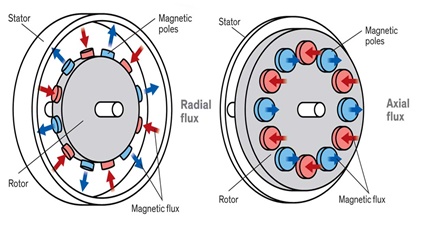
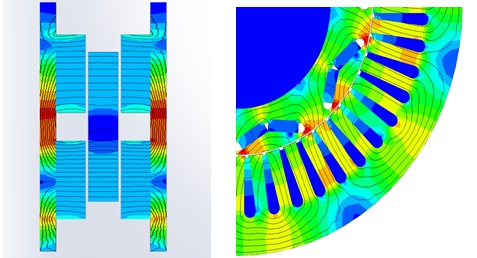
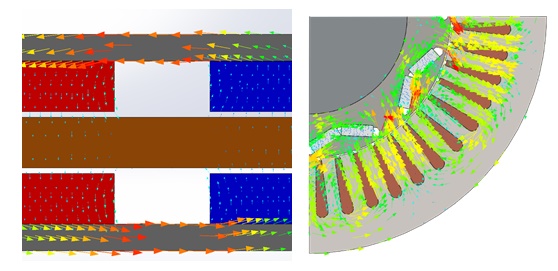
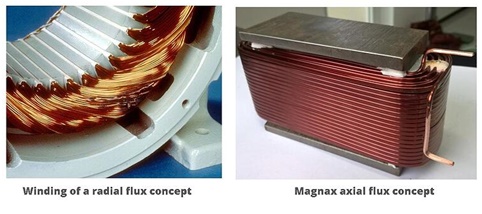
Figure 7 - Comparison between winding of a radial flux concept and Magnax axial flux concept [6]
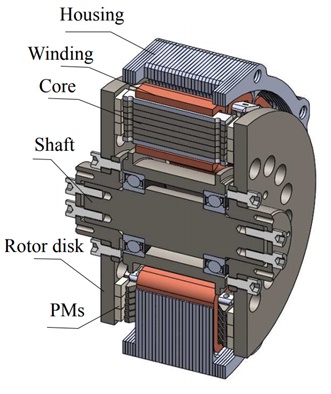
Figure 8 - Example of an axial flux motor with aluminium housing [7]
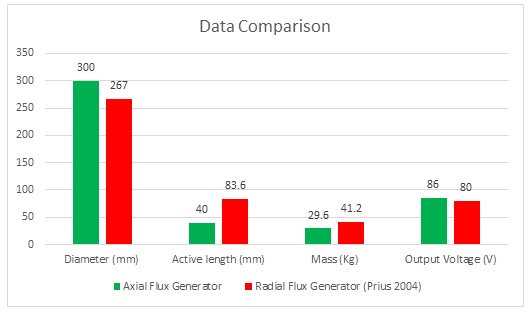
Comparison between two examples of radial and axial flux generators
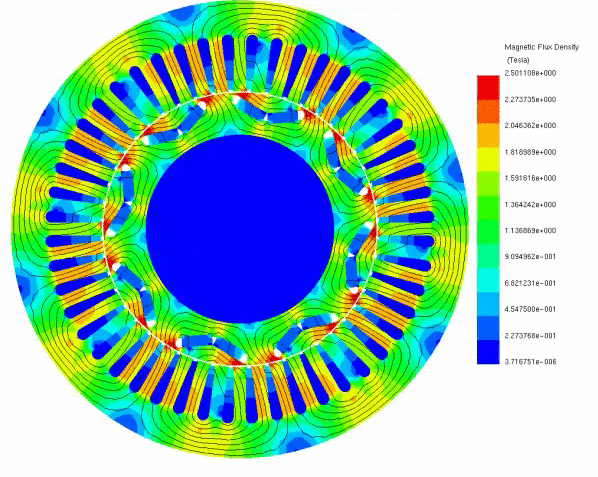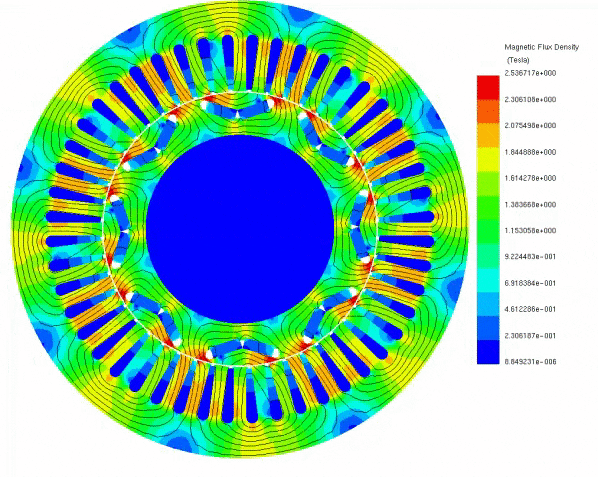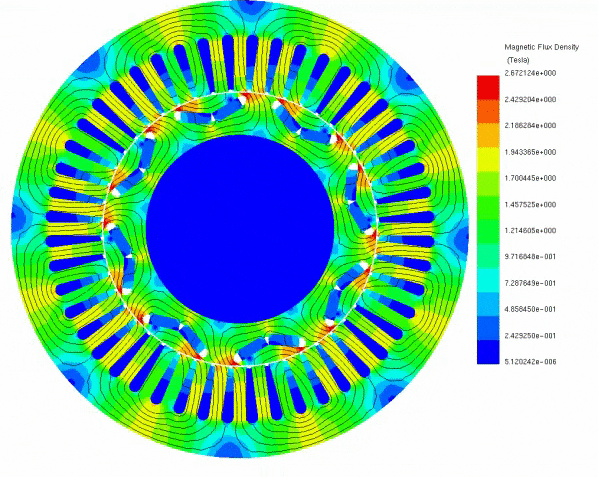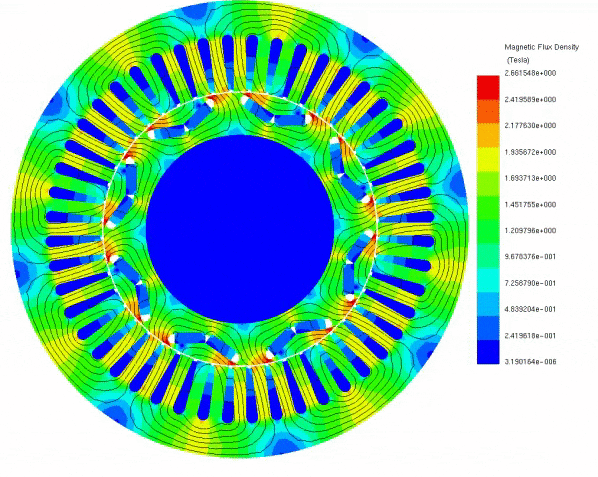
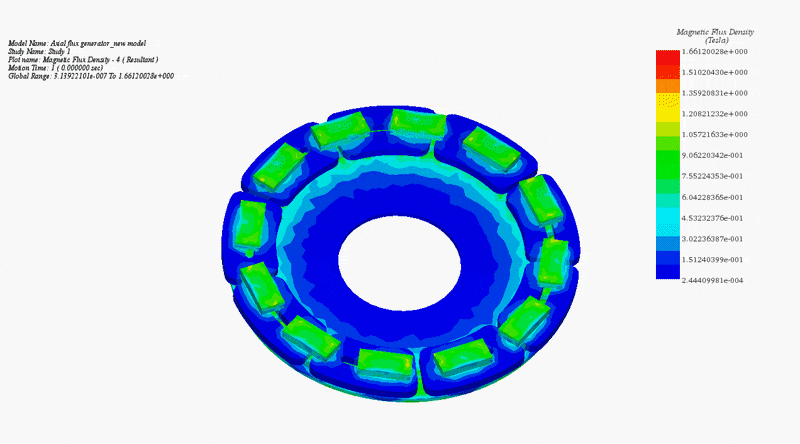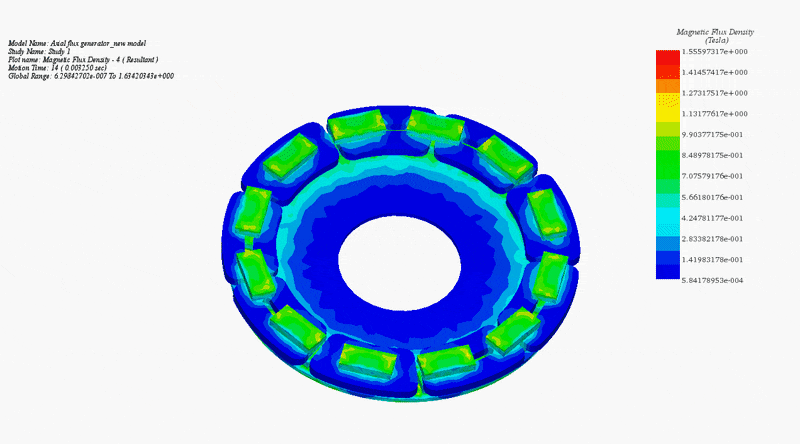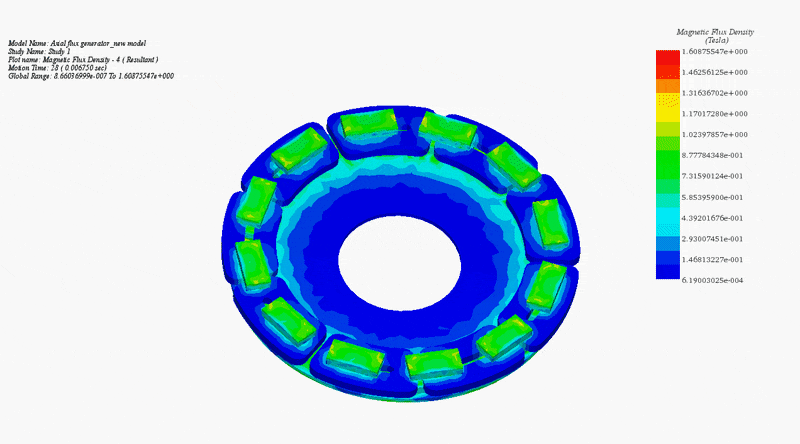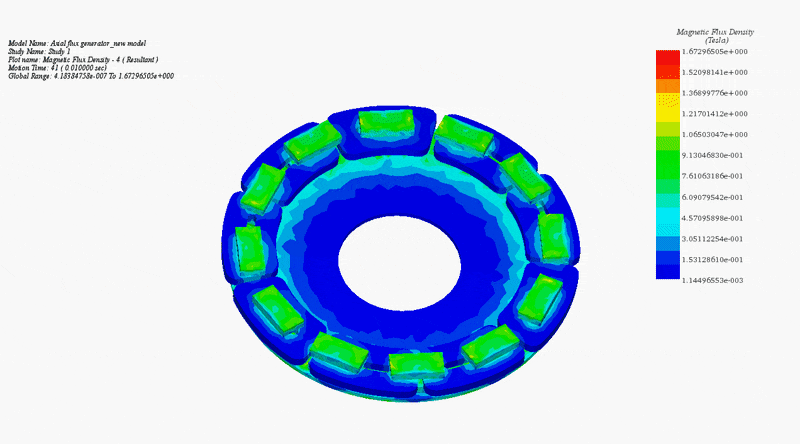
To elucidate the disparity between radial and axial flux machines, EMS was employed for analysis. The study encompassed a radial interior permanent magnet (PM) synchronous machine, akin to the one featured in the 2004 model of the Toyota Prius, and a 24-pole double-sided rotor axial flux generator. These models were seamlessly simulated using EMS. The no-load voltage results reveal that the axial flux machine yields a higher output voltage of 86V compared to the radial PM machine's 80V. Notably, the axial flux machine achieves this higher output power while employing less material and exhibiting a more compact structure.