Transmission system
The transmission system in a vehicle is essential for disconnecting the engine from the road wheels and managing variable speeds. While the engine runs consistently, the transmission adjusts energy output to suit different speeds. It also converts the high-speed, low-torque output from the engine into the lower-speed and higher torque needed for smooth operation through the drivetrain. Crucially, it allows wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns, ensuring stable and controlled handling.
Manual Vs Automatic Transmission
When comparing manual and automatic transmissions, each has distinct advantages and disadvantages. Manual transmissions often come with a lower initial cost and are less expensive to service. Enthusiasts appreciate the control and engagement that manual shifting provides, along with better fuel efficiency and quicker acceleration, qualities that attract race car and performance drivers. However, they require a learning curve, as drivers must master the coordination of the clutch, gas, and shifting, which can be cumbersome in stop-and-go traffic and is less common in the market.
Manual Transmission
On the other hand, automatic transmissions offer ease of use, contribute to less stress during driving, and are highly favored in congested traffic conditions. They are great for beginners, more widely available, and tend to have higher resale values. The drawbacks include a higher purchase price, more expensive repairs, and traditionally lower fuel efficiency compared to manuals, although technological advancements are narrowing this efficiency gap.
Automatic Transmission
Automated Manual transmission
Automated Manual Transmissions (AMT) are mechanically akin to manual transmissions, but they utilize sensors and actuators to automate clutch functions and gear shifts. Electromagnetic actuators, mounted directly on the transmission, manage gear selection and engagement with precision, effectively eliminating the need for a clutch pedal. The advantages of AMTs are noteworthy; they improve fuel efficiency and reduce CO2 emissions, feature a lighter gearbox that's well-suited for electric vehicles, offer enhanced precision with lower fault rates, and are more suitable for heavy-duty applications, making them an increasingly popular choice in modern automotive design.
Cut out illustration of defining components of Isuzu’s automated manual transmission.
Designing a solenoid actuator for an AMT
Designing a solenoid actuator for an AMT presents a set of demanding challenges that require sophisticated engineering solutions. The actuator must achieve a high force density, with capabilities of up to 500N, coupled with rapid actuation times of around 0.3 seconds, ensuring immediate response to force generation commands. Moreover, it is essential to produce this high force at a relatively low operating voltage of 33V, which necessitates an advanced design to maintain high efficiency with minimal losses. Additionally, the system must be designed to manage heat effectively to prevent performance degradation, ensuring consistent operation under varying driving conditions and prolonging the actuator's lifespan.
An AMT CAD model
Overcoming the Design Challenges using EMWORKS
The rigorous demands of designing a solenoid actuator for an AMT are adeptly met with EMWORKS’s simulation software. Faced with the challenge of achieving high force density up to 500N and rapid actuation within 0.3 seconds, EMWORKS allows engineers to meticulously model and simulate the electromagnetic behavior and dynamic response of actuators. The software plays a crucial role in optimizing actuator design for high force output at low voltages, such as 33V, ensuring efficient energy use and minimal losses. EMWORKS’s thermal analysis capabilities are indispensable for predicting and limiting heat generation, a key factor in maintaining actuator longevity and reliability. By providing a comprehensive virtual testing environment, EMWORKS ensures that each design iteration brings engineers closer to a solenoid actuator that meets the AMT’s high-performance standards.
EMWORKS Sample Results for an AMT
Magnetic Flux Density at Different Airgap Distance
Force Results vs Airgap Distance
Force Results vs Housing Thickness
Force Results vs Coil Current
Force Results for Different Materials
Current Vs Time for Different Voltages
Ohmic Loss Vs Time for Different Voltages
Force Vs Time for Different Airgap at Voltage=33V
Speed Vs Time for Different Voltages
Eddy Loss Vs Time for Different Voltages
Magnetic Flux Density with Eddy Off
Magnetic Flux Density with Eddy ON
Eddy Current Density at Voltage = 33V
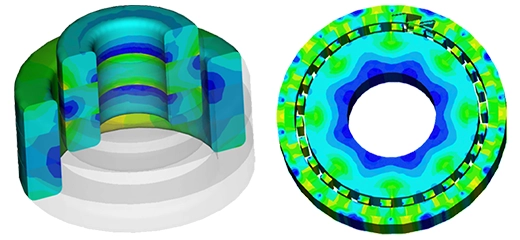
Temperature Distribution in the Coil and Housing
In conclusion, the evolution from manual to automatic, and now to AMT, showcases the relentless pursuit of automotive efficiency, control, and innovation. The role of EMWORKS in designing a solenoid actuator for AMTs is pivotal, providing engineers with the advanced simulation tools necessary to overcome the challenges of force density, actuation speed, and thermal management. Through detailed simulations, EMWORKS ensures that actuators not only meet the required performance standards but also operate efficiently and with durability in mind. The insights gained from simulations inform design decisions that lead to improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and the precision needed for today’s high-performance vehicles.